Controlling Browser Focus and
Scrolling
This document describes the facilities for controlling browser focus and scrolling of HTML pages.
Focus
Focus means that the browser is requested to focus to a particular element; this is implemented by calling the Javascript focus() method on the appropriate element, and is therefore only available when Javascript is enabled. Different browsers implement focus slightly differently, but in general:
- Setting
focus to an enterable field results in the display of a visible cursor and
the user can type directly into the field in question without the need to
tab.
- Setting focus to clickable
elements such as buttons and hyperlinks results in the element being
highlighted in some way e.g. with a dotted line. If the user presses the Enter key when the element is
highlighted, the button or hyperlink is fired.
There are a
number of circumstances that can result in focus being set and these are listed
below in priority order with the highest priority being described first:
1.
Via
scripts using the FPL setfocus
command or API Control.requestFocus() method. These script statements allow application developers to
explicitly set the focus to a specific control. See description
below for further details.
2.
Messages
generated with the FPL message or
corresponding API addxxxMessage() methods. When
warning or error messages are generated by a control-related event, focus is
set to that control.
3.
System
error messages e.g. input validator messages, missing
mandatory fields etc. Focus is set to the control to which the message relates.
4.
Most
recent user action. When the user has performed some action that has caused the
same page to be re-displayed, focus will be set as follows:
- When the action is a change to
a field with the immediate validation option set, focus is set to the next
enterable field (excluding hyperlink and button fields)
- When the action is to click the Add Row button of a table, focus is set to the first enterable column in the new row
- For all other actions e.g. click on button or hyperlink, focus is set to the element that was clicked. Please note that there are some circumstances where it is not posssible to set focus in this way e.g. click on a menu item or a tab in a tabset, and in these instances no focus is set.
5.
Set focus to the first enterable field on the
page – this applies only when moving to a different page. This is configured
using server property Focus To First Field.
Where more
than one focus request exists, the highest priority request is honored. Where
more than one focus request exists at the same level, the first request is
honored, with the exception of the setfocus command where the last request is honored.
FPL setfocus command
The application developer can set focus to an individual
control or field using the FPL setfocus
command, which has the following possible syntaxes:
setfocus controlname [ on pagename] [ERRROR];
setfocus field-name [ : id ] [ [ in ] table table-name ] ] [ on page-name
][ ERROR ];
setfocus $NULL [ on page-name ];
where square brackets [ ] indicate
optional operands. (See FPL Script Command
Syntax for more information)
It is only possible to set focus to a control when Javascript is enabled, and when the control is rendered as an HTML form element of some type. If the control is rendered as more than one form element, then the most obvious element is picked. e.g. for Field Controls, focus is set to the editor portion, not the help image.
For example, the following command sets focus to the
CUSTOMER_NAME control:
setfocus CUSTOMER_NAME;
and the following command sets
focus to the table cell ORDER_AMOUNT on the current row of table ORDERS:
setfocus ORDERS-AMOUNT in table ORDERS;
The ERROR option can be used to apply styling as described
in the next section.
setfocus $NULL can be used to remove all focus from a page.
Each time the command is issued, any existing focus on the
target page is removed. If a control cannot receive focus, e.g. it’s display
only or hidden, the command is ignored.
A setfocus command applies
only to the next display of a page to the end user. All focusing is removed as
the page is displayed.
API focus methods
The application developer can set focus to an individual control by using the Control.requestFocus() method:
controls.FIELDCONTROL1.requestFocus();
fields.CUSTOMER_NAME.fieldControl.requestFocus();
It is only possible to set focus to a control when Javascript is enabled, and when the control is rendered as an HTML form element of some type. If the control is rendered as more than one form element, then the most obvious element is picked. e.g. for Field Controls, focus is set to the editor portion, not the help image.
Focus can be cleared from a page by calling the Page.clearFocus() method:
form.currentPage.clearFocus();
Focus
styling options
Styling can be specified for Standard Focus and Error Focus under Focus Options within the Presentation tab of Form Properties as shown below. Default values for these focus styling properties can be set in the presentation template.
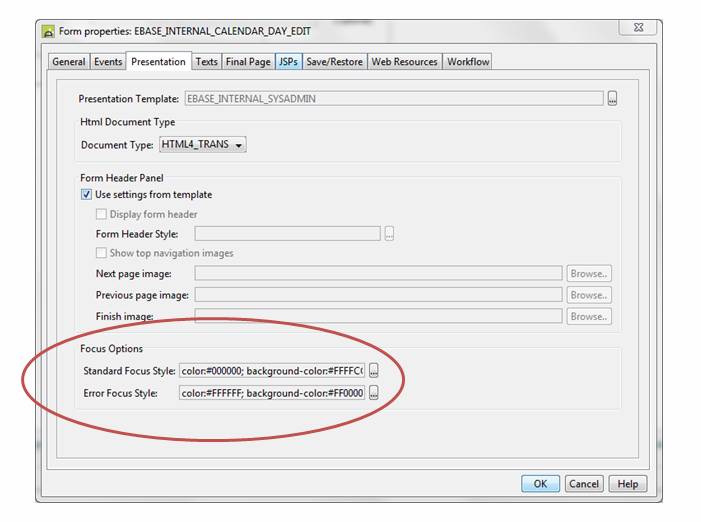
Standard Focus Style is applied when:
·
The end user clicks into an enterable field or
tabs to an enterable field
·
When the system sets default focus to the first
enterable field on a page
·
When the setfocus
FPL command is issued without the ERROR option, or the API Control.requestFocus() method is used
Error
Focus Style is applied when:
·
The system focuses to a control or field in
error. This includes errors resulting from both client side validation such as
checking numeric and date formats, and server side validation such as issuing
of error and warning messages.
·
A setfocus FPL
command is issued with the ERROR option
Error focus
is only applied as a page is initially displayed; if the user subsequently tabs
to a different field and then back to the error field, standard focus is
applied.
Scrolling
Scrolling of a page as displayed in a browser is applicable when the browser window is not large enough to accommodate all of a page’s content; this subject is particularly relevant when a page is re-displayed e.g. as a result of a button click. In overview, the system’s objective is to cause the minimum movement when re-displaying a page i.e. minimize screen “jumping”, but at the same time to ensure that any important information is made visible to the user. Ebase support for scrolling applies to both horizontal and vertical scrolling.
The specific actions performed by the system are listed below in the order they are performed.
1. Scroll to the same screen position as when the request was submitted - this ensures screen stability.
2. Make any focused element visible (see focus).
3. When a table’s Add Row button has been clicked, ensure that the new row is visible.
4. Make warning messages visible.
5. Make error messages visible.
Please note that all these actions, where applicable, are performed in order: the first action ensures screen stability for the user, and for each of the actions 2 – 5 the page is scrolled by the minimum amount to ensure that the item in question is made visible.